What are Heat Pumps?
Heat pumps are the most essential component of your heating and cooling system and yet many homeowners have no idea what they are or how they work. Even though most of your HVAC system may be, out of sight out of mind, maintenance on the entire system is vital, but most important for your system.
Homeowners in the past had to result to a Air Conditioner for cooling and a Furnace for heating. Heat Pumps work in a way that it does both cooling mode and heating mode. A heat pump is an energy-efficient alternative to other types of home heating systems, such as a natural gas furnace or electric baseboards.
Upgrading your current system to heat pumps will also become the new cost effective alternative in 2023. Based on the new SEER2 Efficiency Standard homeowners are expected to save 25-50% on their energy bill by switching to a heat pump.
What are the main types of heat pumps?
There are multiple types of heat pumps that you can choose from. Here is a short description of heat pump systems.
Ductless Mini Split
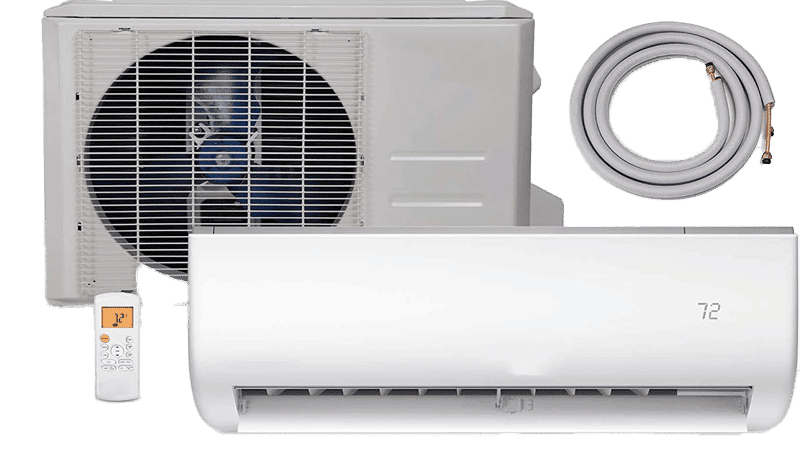
Mini Splits are hvac systems that require no ductwork. The main heat for supplying air is mounted on the wall while the condensing unit is typically located outside.
Split System
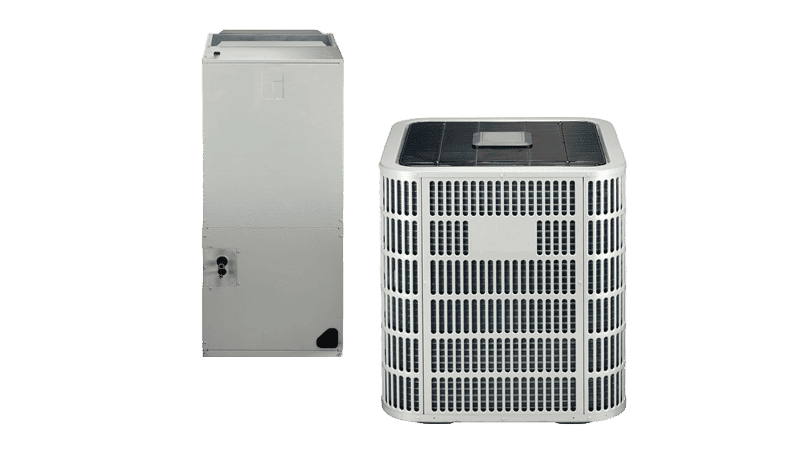
Split system heat pumps are just like mini splits but comes with an Air Handler that is usually located in the attic, garage, or closet. Copper piping transfers refrigerant to the air conditioning condenser located outside.
Packaged Units
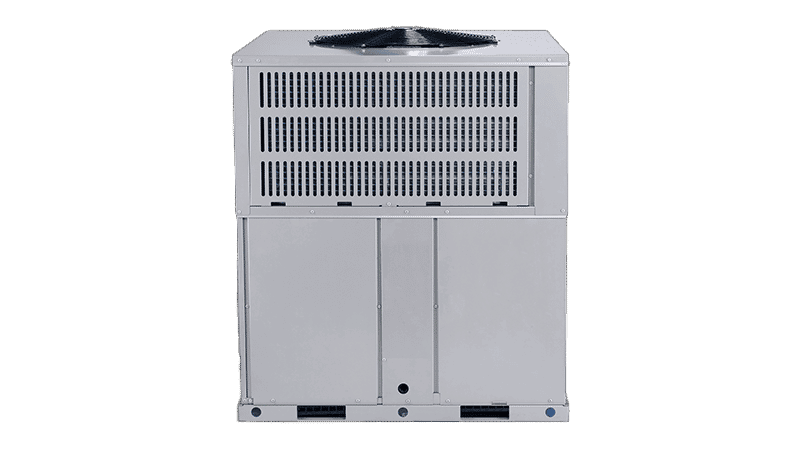

Packaged Unit heat pumps have all the components of a heating and cooling system encased which makes them quit bulky. You will see these units installed on the roof of your home or in some cases the ground taping to the side of your home.
Heat Pump System Variations
Air-source heat pumps
Air source heat pump is type of heat pump transfers heat from the outside air into your home. They are typically less expensive to install and operate than other types of heat pumps.
Geothermal heat pumps
A geothermal heat pump (ground source heat pumps) uses the natural temperature of the earth to either heat or cool your home. These pumps are more expensive to install, but can be more energy efficient in the long run. Geothermal heat pumps are great at keeping a relatively constant temperature.
Water-source heat pumps
A water-source heat pump uses water from a well or a body of water to either heat or cool your home. These pumps are often used in climates where there is a large temperature difference between indoors and outdoors. Water source heat pumps can reach really high efficiencies.
How Does A Heat Pump Work?
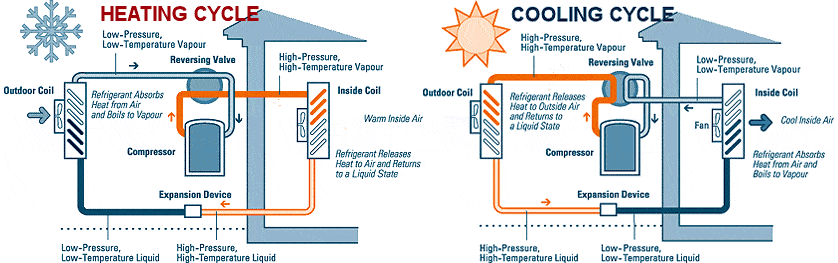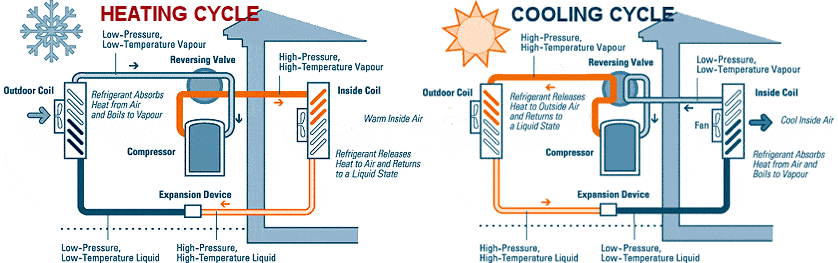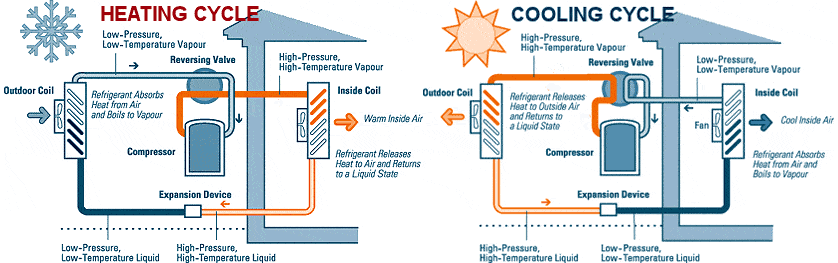
Most people think heat pumps create heat; however, what they do is transfer heat from the outside by using a coolant that circulates between the air handler unit and exterior compressor to transfer heat to warm the home. Heat pumps are also used to cool the home by absorbing indoor heat and transferring it outdoors.
A Heat pump work by using the principles of physics to transfer thermal energy from one place to another. The system consists of three main parts: the compressor, the condenser, and the evaporator. Incoming air is compressed and then heated by the compressor. The hot air is then transferred to the condenser, where it is cooled by passing through a series of coils. The cooled air is then expelled into the room, and the process begins again. Some high-efficiency heat pumps are equipped with a desuperheater , which recovers waste heat from the heat pump's cooling mode and uses it to heat water.
HVAC Heat pumps are common in systems in homes located in more temperature or mild climates where temperatures do not drop below freezing often. Heat pumps can be used in furnaces to make them more energy efficient. If the temperatures reach freezing, heat production will automatically kick over to the furnace. In addition to how the they works, homeowners should know what the various components are to maintain them correctly.
Heat pump components include:
- Outdoor condenser/evaporator unit - The outdoor condenser/evaporator unit is the large metal box that sits outside your house. It contains a compressor, condenser coil, and evaporator coil. The compressor circulates refrigerant through the system, while the condenser coil and evaporator coil cool the air. The evaporator absorbs heat and transfers it outside the unit. In short, the purpose of these systems is for heat transfer from one place to another.
- Indoor fan - The indoor fan is responsible for pushing the air around inside of the house. It helps to circulate the air and keep things comfortable.
- Refrigerant - Refrigerant is the coolant used in air conditioners and heat pumps to transfer thermal energy from the indoors to the outdoors. In most residential and commercial units, the refrigerant is a gas that circulates between two coils: an indoor coil and an outdoor coil. The indoor coil absorbs heat from the air in your house or office, and the outdoor coil releases that heat into the environment.
- Compressor - The compressor is a critical component of the heat pump. It is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas and moving it through the system. This helps to increase the pressure and create heat
- Reversing valve - The reversing valve is a critical component of a heat pump. It allows the system to switch between heating and cooling modes. When the system is in heating mode, the reversing valve directs refrigerant to flow of liquid or gas refrigerant in a reverse direction, allowing it to absorb heat from the air and then release it into the indoors. When the system is in cooling mode, the reversing valve directs refrigerant to flow in the normal direction, allowing it to remove heat from the indoors and release it outdoors.
- Expansion valve - The expansion valve is a component of the refrigeration system that regulates the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator. It allows the refrigerant to expand as it passes from the high-pressure side of the system to the low-pressure side, which helps to maintain the correct pressure and flow within the system.
SEER2 Efficiency Standard Changes in 2023 and how the affect Heat Pumps
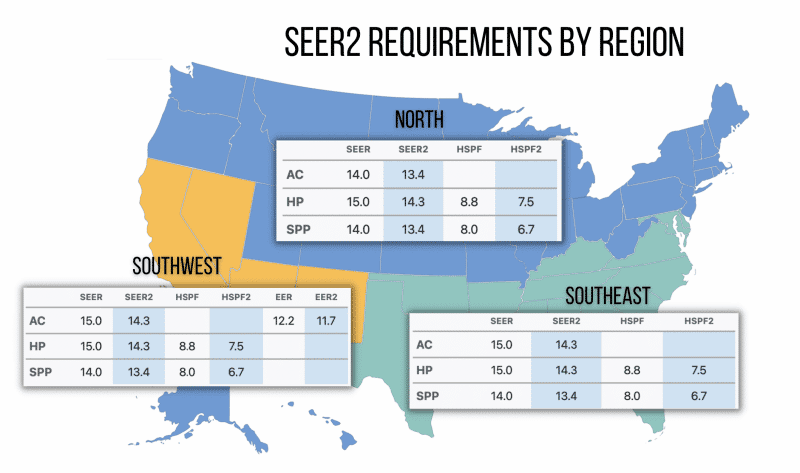
The Department of Energy (DOE) has announced that the SEER2 efficiency standard will be changing in 2023. This change will affect all heat pumps, so it’s important to understand what it means for you and your home.
The SEER2 efficiency standard is the measure of how efficient a heat pump system is at converting electricity into heat. The higher the SEER2 rating, the more efficient the heat pump is. In 2023, the DOE will be increasing this rating from 14 to 16.
This change will mean that all heat pumps sold in the US must have a SEER2 rating of 16 or higher. If you have an older heat pump, it may not meet this new standard. You may need to replace your old heat pump with a newer, more efficient model in order to continue using it.
If you’re considering purchasing a heat pump, be sure to check its SEER2 rating to make sure it meets the new standard. You may also want to consider upgrading to a model that has a higher rating, as these will be more energy-efficient and could save you money on your energy bills.
Fortunately for Balanced Comfort locals, we are the Top Bosch Heat Pump Installers in the central valley with heat pumps with a rating of 18+. Request a free quote today to get a heat pump system installed.
How Efficient are Heat Pumps?
Department of Energy (DOE) has stated that homeowners switching to Heat Pump systems are reducing their energy bills by 25%-50%.
In addition to being energy efficient, there are several other advantages to using a heat pump in your home. First, because they don't create new heat, they don't produce greenhouse gases like some other types of heating systems do.
That makes them more environmentally friendly than those other options. Also, because they move existing heat rather than creating new heat, they tend to be very quiet. And finally, they can provide both heating and cooling for your home, which can save you money on your utility bills.
If you're looking for a way to make your home more efficient, consider installing a heat pump. Heat pumps are devices that transfer existing heat from one place to another and they come in two main types: air-source and ground-source.
Both types of heat pumps are energy efficient, but ground-source models are slightly more so. In addition to being energy efficient, there are several other advantages to using a heat pump in your home including that they don't produce greenhouse gases, they tend to be very quiet, and they can provide both heating and cooling for your home.
Cost-effective
One of the primary benefits of heat pumps is that they are cost-effective. Heat pumps use a small amount of energy to move heat from one place to another, which makes them much more efficient than other systems. As a result, heat pumps can help to save you money on your energy bills.
Environmentally friendly
Heat pumps are also environmentally friendly. Because they use a small amount of energy, they produce fewer greenhouse gases than other air conditioning systems. Additionally, heat pumps can help to reduce the amount of energy that your home uses, which can further help to protect the environment.
Versatile
Heat pumps are also versatile and can be used for heating and cooling your home. In the winter, heat pumps move heat from the ground or air into your home, and in the summer, they do the reverse and move heat from your home into the ground or air. This makes heat pumps an ideal solution for climate control in all seasons.
Low maintenance
Heat pumps are low maintenance and do not require regular tune-ups or repairs like other heating and cooling systems. Additionally, most heat pump heating system come with a warranty, so you can be sure that your investment is protected.
Improves indoor air quality
Another benefit of heat pumps is that they improve indoor air quality by circulating fresh air throughout your home. This can help to reduce allergens and pollutants in the air and create a healthier indoor environment for you and your family
Where Does The Heat Come From?
When it comes to colder climates the heat pump extracts heat from the surrounding outdoor air and delivers it inside. The compressor in the heat pump compresses the refrigerant, raising its temperature. The hot refrigerant then flows into the coil in the furnace, where it releases its heat. The cooled refrigerant then flows back to the heat pump, where it is compressed again and the cycle repeats.
Are Heat Pumps Location-Specific?
Heat pumps are not location-specific, but the way they work does depend on the climate. In climates with severe winters, a heat pump will work as an air conditioner in the summer and a heater in the winter. In climates with mild winters, a heat pump can be used for heating and cooling.
What is the difference from Heat Pumps and Furnaces?
Now that you know the basics of heat pumps, you may be wondering if you should buy one for your home. Here are a few things to consider:
Heat Pump Cost: A heat pump costs more than a furnace, but it can save you money in the long run because it uses less energy and doesn't need combustion of natural gas of air conditioners.
A heat pump costs more than a furnace, but it can save you money in the long run because it uses less energy.
Energy Efficiency: A heat pump is more efficient than a gas furnace, so you’ll use less energy to heat your home.
Heat pumps are more efficient than a furnace, so you’ll use less energy to heat your home. Size: A heat pump is bigger than a furnace, so make sure you have enough space in your home to install one. heat pumps rely on electricity only to operate.
While heat pumps are bigger than a furnace, so make sure you have enough space in your home to install one. Climate: A heat pump is not as effective in cold climates as a furnace is, so make sure you live in a climate where a heat pump would be effective.
If you decide that a heat pump is the right choice for your home, make sure to research the different types available and find the one that best meets your needs.
Benefits of having a Heat Pump For Your Home?
A heat pump is a great option for your home if you are looking for an efficient way to heat and cool your home. Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another, so they can be used to heat your home in the winter and cool it in the summer. They are also a great option if you are looking for an better way to heat and cool your home, as they can be up to three times more efficient than traditional central air systems.
- Heat pumps will save you money on your energy bills.
- Reduce your carbon footprint.
- Heat pumps can provide heating and cold air for your home.
- Can be used in any climate, even cold climates.
- Very efficient way to heat and cool your home.
- Heat pumps can last for many years with proper maintenance.
- They are much quieter than a traditional furnace or air conditioner.
- Heat pumps doesn’t produce any emissions, so it’s better for the environment.
- Improve the indoor air quality in your home.
- A heat pump can be used in conjunction with solar panels to further reduce your energy bills
- Doesn't require gas compares to a gas furnace
- Best energy efficiency in the market
Maintenance is KEY to Efficient Heat Pump Systems

To maintain each of these components as well as the heat pump as a unit, there is a specific maintenance schedule that must be followed. During winter months you should ensure there is no ice or snow build up that would restrict air flow. During the remaining months of the year maintenance will include these steps:
- Removing foliage, trimming shrubs away from the unit.
- Make sure pump is elevated at least four inches off the ground.
- Ensure there are no gutters leaking above the unit.
- Clean or replace filters at monthly.
- Make sure registers are open.
- Clean outdoor coils if they look dirty.
Many professional HVAC companies will offer scheduled preventative maintenance for your heat pump and HVAC unit. Check-ups should happen once per year, but twice is preferable. Fall and Spring are the best times for maintenance and help prepare for the times of year when the heat pump will work the hardest-Winter and Summer.
A maintenance technician will inspect the ducts, coils, blower, filters, and other parts of your system in addition to the heat pump. They will also ensure that there is no duct leakage, and the refrigerant is charged sufficiently and replaced if necessary. Motor lubrication, belt inspection and replacement, and inspecting drain holes and thermostats are all a part of preventative maintenance.
All these tasks sound like a lot to remember and take care of which is why you need a professional HVAC company to handle these vital steps for you at least once per year to meet your heating and cooling requirements.
FAQ
During cold temperatures, heat pumps heating mode works by transferring heat from the conditioned space to outdoor air. In the summer, they move heat from inside your house to the outdoors heating season. This process cools your house down. In the winter, they do the opposite and move heat from outside your house to inside.
